In conclusion, managing labor costs requires a strategic strategy that balances efficiency, productivity, and employee engagement. By implementing the methods outlined above, companies can optimize their labor bills, remain aggressive within the market, and keep profitability. Nevertheless, another essential issue to contemplate is how labor costs differ from price of residing. Mounted costs are bills that don’t change, regardless of how a lot your small business is producing or selling. These costs are the same every month or 12 months, making them predictable and easy to price range for.
- Let’s say the variable costs in a factory that makes clothes are the fabric and labor used to make the dresses.
- On the other hand, variable prices are immediately associated to the level of manufacturing or gross sales.
- These FDs offer attractive rates of interest, flexible tenures, and guaranteed returns, making them a sensible selection for steady and safe financial development.
- This contains manufacturing workers, engineers, and meeting line workers whose labor is well traceable to particular outputs.
Variable components, while more complex to manage, might help management costs and enhance productivity by instantly linking pay to efficiency. Variable costs change instantly in relation to the output of a enterprise, so when there is no output, there are no variable costs. A good example of variable prices is the operational bills that improve or decrease primarily based on the business activity. If a business grows, so will its bills corresponding to utility payments for electricity, gasoline, or water. Fixed prices check with predetermined expenses that can stay the identical for a particular interval and are not influenced by how the enterprise is performing. Since most companies will have sure mounted prices regardless of whether or not there is any enterprise exercise, they are simpler to finances for as they stay the same all through the financial 12 months.
Conversely, if the allocation is skewed in course of bed frames, customers may pay more for these merchandise than needed. Incorrect pricing may end up in lower profits or a loss of market share if rivals supply related merchandise at higher prices. Inaccurate allocation of those labor costs could lead to undercosting or overcosting, which may adversely have an result on product pricing and general profitability. A fastened cost is one that stays the same each month no matter how a lot you’re selling.
Impact On Business Decisions

These costs are easier to hint back to a particular product and could be influenced by altering production volumes. For occasion, hourly wages for meeting line staff or the price of extra time pay fall under this category. Direct labor prices, often known as manufacturing labor, are directly attributed to employees actively involved in making a product. This consists of hourly wage earners on an meeting line or those liable for building and fabricating parts. Direct labor prices can be easily determined by calculating the sum of wages paid to these staff. For instance, if XYZ Furniture employs ten staff to assemble eating room chairs and pays them a mixed wage of $20,000 per 30 days, the direct labor value for this product is $20,000.
Advantages Of Variable Salary
Instead, adjustments can stem from new contractual agreements or schedules. A fixed value is a business expense that does not differ even when the extent of manufacturing or sales modifications given a particular related range. Variable prices are often described as “per unit” costs since they are calculated on a per-unit basis. For instance, if a company produces a hundred items of a product and the variable price per unit is $5, the total variable value for that production run would be $500. If the corporate decides to increase production to 1,000 items, the whole variable price would enhance to $5,000. Assuming the corporate employs 10 laborers, and the minimum wage within the state is $8, the corporate has a set price of salaries of $80 per hour.
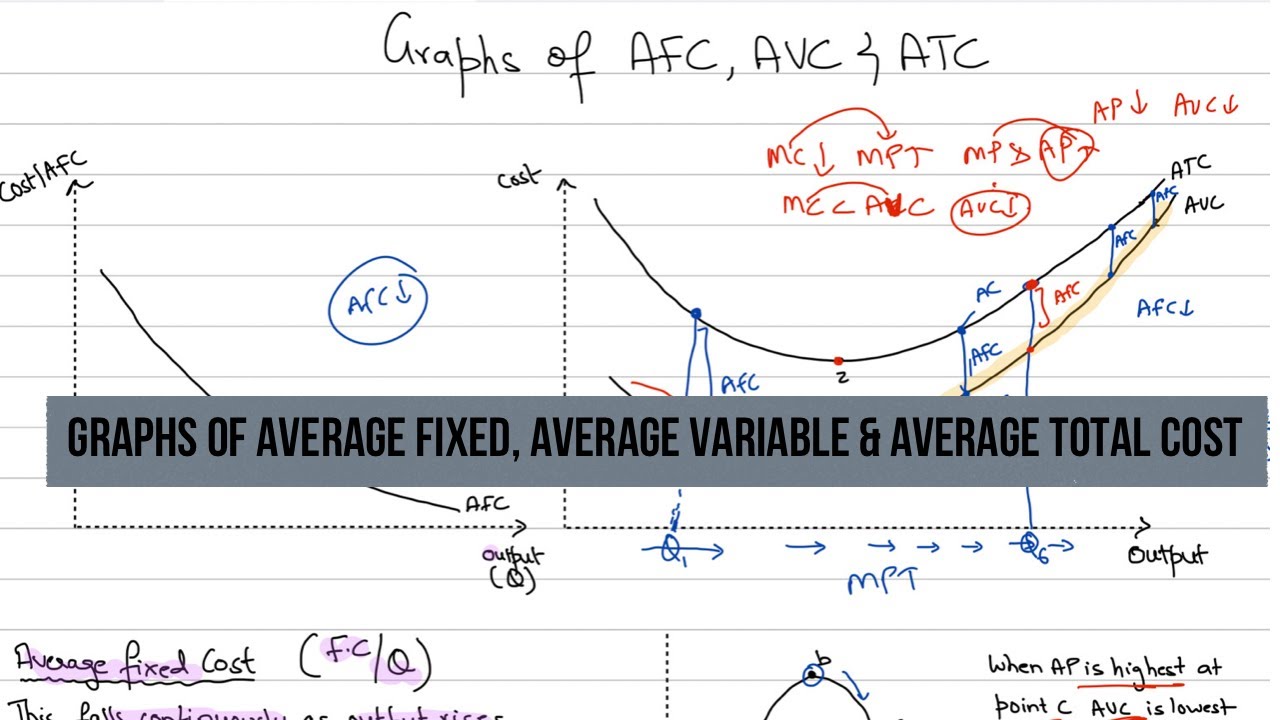
This differentiation is essential in understanding fastened prices higher. The more a company produces, the mounted price remains the same. Effective budgeting is crucial for managing both mounted and variable costs in a small enterprise. Fastened and variable costs are two distinct classes of expenses that businesses incur of their operations, every with distinctive characteristics and implications for monetary management.
They aren’t only a reflection of the worth an organization places on its employees but in addition a key think about monetary planning and sustainability. Another example of variable prices could be if a business produces hats at $5 each. If the enterprise produces 200 units, its variable price could be $1,000.
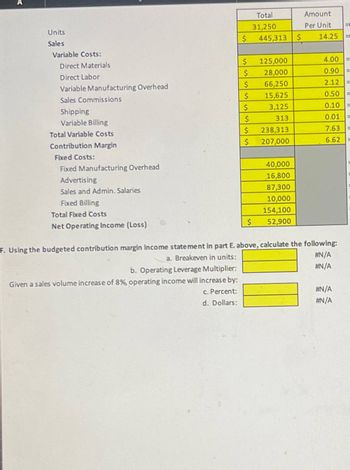
You can calculate the variable price for a product by dividing the total variable expenses by the number of items for sale. To decide the fixed price per unit, divide the entire https://www.simple-accounting.org/ fastened cost by the variety of units for sale. Variable prices may be challenging to handle as they can differ from month to month, increase or lower shortly, and have a more direct impact on revenue than mounted costs.
All sunk costs are fixed prices in financial accounting, however not all mounted costs are thought-about to be sunk. The defining characteristic of sunk prices is that they can’t be recovered. Variable salary is the performance-driven portion of your revenue that fluctuates based mostly on individual, staff, or company achievements. It serves as an incentive to encourage employees and aligns their efforts with organisational targets. They’re typically one of many largest fixed costs you will deal with. Let’s dig into how they fit into your organization’s expenses and why you should concentrate.
For instance, predictive analytics can be utilized to forecast turnover charges and perceive the impression on wage bills. There are many ways in which a enterprise can scale back its variable costs. For occasion, increasing output using the identical quantity of material can dramatically reduce down costs, provided the standard of goods is not impacted.



Leave a comment